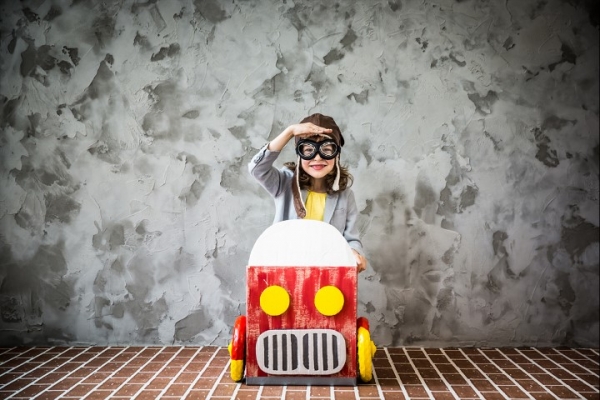
Κέντρο έρευνας (16)
Σημαντική ανακοίνωση επαναλειτουργίας του κέντρου "Μαθαίνω παίζοντας"
Γράφτηκε από Άρης (Βλαστάρης) ΤσακίρηςΑγαπητοί μας γονείς,
Θα θέλαμε να σας ενημερώσουμε ότι το Κέντρο μας έχει ξεκινήσει και πάλι την λειτουργία του.
Πρέπει όλοι μας να είμαστε πολύ προσεκτικοί για να αποφύγουμε τυχόν διάδοση του ιού COVID-19.Όσον αφορά το Κέντρο μας, θα ακολουθήσουμε τα παρακάτω:
- Οι συνεδρίες είναι εξατομικευμένες με την παρουσία μόνο του παιδιού και του θεραπευτή στην αίθουσα.
- Κατά τη διάρκεια της συνεδρίας γίνεται χρήση μάσκας και γαντιών μιας χρήσης. Οι αίθουσες αερίζονται και μετά το πέρας κάθε θεραπείας γίνεται απολύμανση των επιφανειών και των καθισμάτων.
- Είναι πολύ σημαντικό να μην υπάρχουν καθυστερήσεις, έτσι ώστε να μην συγχρωτίζονται στον χώρο πολλά άτομα αλλά και για να προλαβαίνουν οι θεραπευτές να κάνουν τις παραπάνω διεργασίες.
- Στην είσοδο υπάρχει για άμεση χρήση αντισηπτικό αλκοολούχο διάλυμα. Συνίσταται καλό τρίψιμο των χεριών μέχρι να στεγνώσει το αντισηπτικό.
- Με την είσοδο στο χώρο του Κέντρου μας , παρακαλούμε να πλένετε άμεσα και πολύ σχολαστικά τα χέρια στα παιδιά σας.
- Αποφεύγουμε τις άσκοπες μετακινήσεις μέσα στο χώρο.
- Σε περίπτωση που το παιδί δεν νιώθει καλά, ενημερώνουμε έγκαιρα τον θεραπευτή και ζητάμε την ακύρωση του ραντεβού.
Είμαστε στη διάθεση σας να συζητήσουμε οποιοδήποτε προβληματισμό σχετικά με τα παραπάνω μέτρα και να θέσουμε και επιπλέον μέτρα αν νιώσουμε ότι χρειάζεται.
Είμαστε μαζί σε όλο αυτό και θα βγούμε όλοι μαζί πιο δυνατοί.
Με εκτίμηση,
Μαθαίνω Παίζοντας
Τι μας διαφοροποιεί;
Γράφτηκε από Άρης (Βλαστάρης) ΤσακίρηςΕίναι λογικό οι γονείς και οι κηδεμόνες παιδιών και εφήβων με διάφορες αναπτυξιακές και άλλες δυσκολίες να μην έχουν πάντα τις απαραίτητες πληροφορίες για να κρίνουν ποιος χώρος είναι ο πλέον κατάλληλος για να καλύψει τις ανάγκες τους. Εμείς, λοιπόν, θα σας παρουσιάσουμε εν συντομία τα στοιχεία που μας διαφοροποιούν:
- Ειδικευόμαστε στις αξιολογήσεις και στις διαγνώσεις παιδιών που γίνονται με έγκυρα και σταθμισμένα διαγνωστικά εργαλεία. Δεν είναι τυχαίο ότι η δρ Ευφροσύνη Καλύβα είναι επιστημονική συνεργάτης της Α’ Παιδιατρικής Κλινικής του Ιπποκράτειου Νοσοκομείου Θεσσαλονίκης και έχει τεράστια κλινική εμπειρία. Τα αποτελέσματα αυτών των διαγνώσεων χρησιμοποιούνται και για τον σχεδιασμό εξατομικευμένων θεραπευτικών προγραμμάτων αλλά και για την παρακολούθηση της εξέλιξης του παιδιού.
- Παράγουμε και δεν αναπαράγουμε απλώς γνώση. Αν διαθέσετε τον χρόνο να ρίξετε μια ματιά στην κατηγορία δημοσιεύσεις στην ιστοσελίδα μας, θα δείτε ότι έχουμε γράψει βιβλία στα Ελληνικά και στα Αγγλικά, κεφάλαια σε βιβλία και άρθρα σε ξενόγλωσσα επιστημονικά περιοδικά με κριτές. Ένα κομμάτι αυτής της δουλειάς έχει γίνει σε συνεργασία με έγκριτους πανεπιστημιακούς τόσο στην Ελλάδα όσο και στο Εξωτερικό. Το βιβλίο της δρ Ευφροσύνης Καλύβα για τις εκπαιδευτικές και θεραπευτικές προσεγγίσεις στον αυτισμό που κυκλοφορεί και στα Αγγλικά από το 2011 αναγορεύτηκε πρόσφατα από την Αμερικάνικη Ένωση Βιβλιοθηκών ως ένα από τα 12 βιβλία της τελευταίας 10ετίας για τον αυτισμό που θα πρέπει κάποιος να διαβάσει. Πολλά αποσπάσματα από το συγκεκριμένο βιβλίο φιλοξενούνται αυτούσια και σε σχετικές ιστοσελίδες (www.autismgreece.gr). Έχουμε συμμετάσχει επίσης σε περισσότερα από 100 Ελληνικά και διεθνή επιστημονικά συνέδρια με προφορικές εισηγήσεις (συχνά ως προσκεκλημένοι ομιλητές).
- Επιμορφώνουμε γονείς, εκπαιδευτικούς και άλλους επαγγελματίες ψυχικής υγείας. Εδώ και 15 χρόνια συμβάλλουμε στην επιμόρφωση με ημερίδες, εργαστήρια, ομιλίες, εκπαιδευτικά προγράμματα και ποικίλες άλλες δράσεις τόσο στην Θεσσαλονίκη όσο και σε άλλες πόλεις της Βόρειας Ελλάδας. Η δρ Ευφροσύνη Καλύβα ήταν Αναπληρώτρια Καθηγήτρια ψυχολογίας σε προπτυχιακό και μεταπτυχιακό επίπεδο από το 2000 έως και το 2017 στο Διεθνές Τμήμα του Πανεπιστημίου του Sheffield, CITYCOLLEGE. Δίδαξε στο Διδασκαλείο Γληνός δασκάλους ειδικής αγωγής από το 2002 έως και το 2012 που έκλεισε πλέον το τμήμα και υπήρξε λέκτορας με καθεστώς ΠΔ/407 στο τμήμα Εκπαιδευτικής και Κοινωνικής Πολιτικής του Πανεπιστημίου Μακεδονίας όπου δίδαξε και σε προγράμματα εξειδίκευσης 300 ωρών.
- Σταθμίζουμε εργαλεία πρώιμης ανίχνευσης αναπτυξιακών διαταραχών στην Ελλάδα. Ο καθηγητής Matson από το Πανεπιστήμιο της Λουιζιάνα μας επέλεξε για να σταθμίσουμε στα Ελληνικά το BISCUIT και το πανεπιστήμιο του Γκέτενμπουργκ στην Σουδία για να σταθμίσουμε το ATAC. Αυτό είναι πολύ τιμητικό για εμάς εφόσον έχουν επιλεχθεί ελάχιστοι επιστήμονες σε παγκόσμιο επίπεδο και αποτελεί μια σημαντική διάκριση με την οποία θα βοηθήσουμε έμπρακτα τα παιδιά με αναπτυξιακές δυσκολίες και τις οικογένειές τους.
- Έχουμε λάβει επιδοτήσεις από την Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση για να διεξάγουμε έρευνα σχετικά με τα δικαιώματα των παιδιών. Κάποια από τα προγράμματα αυτά έχουν ολοκληρωθεί ενώ άλλα είναι σε εξέλιξη και έχουμε συν-γράψει και έναν οδηγό στα Ελληνικά για το πως μπορούμε να προσεγγίσουμε παιδιά και νέους που έχουν βιώσει βία και παραμέληση.
- Επιδεικνύουμε ευθύνη προς την κοινωνία προσφέροντας τις υπηρεσίες μας δωρεάν σε συλλόγους που ασχολούνται με το παιδί καθώς και σε ορισμένους γονείς που δεν έχουν την οικονομική δυνατότητα να παρέχουν τις απαραίτητες υπηρεσίες στα παιδιά τους.
Όλα τα παραπάνω αποτελούν μια έξωθεν μαρτυρία για την ποιότητα των υπηρεσιών που παρέχουμε και έχουν τύχει ευρείας αναγνώρισης και από την διεθνή επιστημονική κοινότητα. Είναι επίσης αυτό που μας κάνει διαφορετικούς.
Προβλήματα συμπεριφοράς
Γράφτηκε από Άρης (Βλαστάρης) ΤσακίρηςΠροβλήματα Συμπεριφοράς
Πολλά παιδιά προσχολικής και σχολικής ηλικίας εκδηλώνουν προβλήματα ανεπιθύμητης ή ανάρμοστης συμπεριφοράς, τα οποία ορισμένες φορές μπορεί να οφείλονται στην έλλειψη ορίων από το περιβάλλον και στην προσπάθεια του παιδιού να τραβήξει την προσοχή. Οι γονείς πρέπει να αρχίσουν να ανησυχούν όταν η κατάσταση του παιδιού τους ξεφεύγει από τα όρια σε τέτοιο βαθμό, ώστε να εμποδίζει την ομαλή λειτουργία της οικογένειας και να οδηγεί το παιδί σε προβληματικές διαπροσωπικές σχέσεις. Το ποσοστό των παιδιών που παρουσιάζουν ήπια ή πιο σοβαρά προβλήματα συμπεριφοράς ανέρχεται στο 7-9% του μαθητικού πληθυσμού και η διάγνωση γίνεται κυρίως με κλίμακες που καλούνται να συμπληρώσουν οι γονείς και οι εκπαιδευτικοί. Και εδώ χρειάζεται ιδιαίτερη προσοχή για την ποιοτική αξιολόγηση των συμπεριφορών, ώστε να δοθεί μία σωστή διάγνωση προβλημάτων συμπεριφοράς.
Τα συμπτώματα που εκδηλώνουν τα παιδιά με προβλήματα συμπεριφοράς είναι τα ακόλουθα:
1) Τα παιδιά αρνούνται να συμμορφωθούν με κανόνες και να υπακούσουν είτε τους γονείς τους είτε άλλους ενήλικες.
2) Τα παιδιά έχουν μία έντονη αρνητική διάθεση για να συνυπάρξουν και να συνεργαστούν με άλλους ανθρώπους, με αποτέλεσμα να δημιουργούνται συχνά έντονοι καβγάδες.
3) Τα παιδιά με προβλήματα συμπεριφοράς προκαλούν συχνά και είναι ιδιαίτερα αντιδραστικά, ενώ συνηθίζουν να λένε ψέματα για να αποφύγουν την τιμωρία.
4) Εκδηλώνουν έντονη επιθετικότητα σε ανθρώπους και ζώα και προβαίνουν συχνά σε φθορά ή καταστροφή ξένης περιουσίας.
5) Εμπλέκονται συχνά σε απάτες ή κλοπές αντικειμένων, η αξία των οποίων αυξάνει ανάλογα με την ηλικία τους, με αποτέλεσμα να έχουν προβλήματα με τον νόμο.
Πρέπει να σημειωθεί ότι ο βαθμός στον οποίο εκδηλώνονται οι προαναφερθείσες συμπεριφορές διαφέρουν από παιδί σε παιδί (και ενίοτε από πλαίσιο σε πλαίσιο) και για τον λόγο αυτό είναι απαραίτητο να γίνεται σωστή αξιολόγηση και διάγνωση με τα κατάλληλα εργαλεία και την ενεργό συμμετοχή των γονέων του παιδιού.
Παρουσιάσεις σε επιστημονικά συνέδρια (με χρονολογική σειρά)
Προσεκλημένοι ομιλητές
▪ Kalyva, E. (1999). Psychosocial Influences on Adolescent Smoking: Proposals for Intervention Programmes. Invited Speaker. Paper presented at the Conference organised by the Greek Pedagogical Institute. The proceedings of the conference will be published and distributed to all the Greek secondary schools.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). The importance of play in autism. Invited Speaker at RNIB Annual Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Helping children with autism and their families through play. Invited Speaker at the Annual Portage Conference in Northampton.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2003). Adolescents and smoking: Knowledge and misconceptions. Paper presented at an invited symposium on ‘Adolescents; and teachers’ perceptions of mental health illness, addiction, and difference’ during the 1st Conference of the Psychological Society of Northern Greece in Volos, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2005). Educating children with autism. Invited Speaker at a Day Conference on “Special Needs Education in Primary Education: Educational Reality and Future Perspectives”, University of Macedenia.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2006). Research methods in special needs education. Invited Speaker at a Day Conference on “Directions of Special Needs Education in Greece” at Aristotle University, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Κalyva, E. (2006). Behavioural problems in children with learning disabilities. Invited Speaker at the Panhellenic Conference entitled: “Learning disabilities: Right to life, right to knowledge” in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Κalyva, E. (2007). Symptoms of learning disabilities in the preschool years.. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Nursery School “Kokkinoskoufitsa” in Panorama of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Κalyva, E. (2007). Educating adults with special educational needs. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Municipality of Ampelokipi in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). The Circle of Friends: Training children with behavioural problems in social skills. Invited Speaker at the Conference on “Contemporary Approaches to Special Needs and Education” organised by the National Association of Special Needs Educators in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Κalyva, E. (2008). Early identification of special educational needs.. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Nursery School “Kokkinoskoufitsa” in Panorama of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). The Circle of Friends: Training children with behavioural problems in social skills. Invited Speaker at the Conference on “Contemporary Approaches to Special Needs and Education” organised by the National Association of Special Needs Educators in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Educating children with learning disabitlities in the classroom. Invited Speaker at the Conference on “Training children with special needs” organised by the Educational Municipality of Kavala, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). The Circle of Friends: Training children with behavioural problems in social skills. Invited Speaker at the Conference on “Contemporary Approaches to Special Needs and Education” organised by the National Association of Special Needs Educators in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Educating and teaching children with autism. Invited Speaker at the 1st Conference of the Association of Parents of Children with Autism in Serres, Greece.
▪ Vivas, A.B., Angeles, F., & Kalyva, F. (2008). Training with differential Outcomes is effective in children with developmental dyslexia. Invited oral presentation in a symposium at the XXIX International Congress of Psychology, 20-25 July, Berlin, Germany.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Autism: Early signs and how to diagnose it. Invited Speaker at the 1st International Conference entitled: “Autism in Albania: Pubic awareness and public responsibility” in Tirana, Albania.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Comparison of eating attitudes between adolescent girls with and without Asperger's Syndrome: Daughters’ and mothers’ reports. Invited Speaker at the Autism 2008 Online AWARES Conference on Autism organised by the Wales International Autism Association, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). The social includion of a child with Asperger syndrome. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Municipality of Thessaloniki and the Administration of Public Libraries of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Autism and Asperger syndrome: Educational and therapeutic approaches. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Municipality of Thessaloniki and the Administration of Public Libraries of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Κalyva, E. (2009). Setting limits and boundaries in the adult-child relationship.. Invited Speaker at a Seminar organised by the Nursery School “Kokkinoskoufitsa” in Panorama of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2009). Patient with Alzheimer and caregiver of an adult with Asperger Syndrome: A case study. Invited Speaker at the 6th Panhellenic Conference of Alzheimer and Related Disorders in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2009). Educational approaches for autism and behavior problems.. Invited Speaker at an Educational Seminar organized by the Local Educational Authority of Larisa, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2009). Teachers' Perspectives of the Sexuality of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Invited speaker at the Online Awares Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2010). The Relationship Between Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Mental Health Professionals. Invited speaker at the Online Awares Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papageorgiou, V. (2011). What do Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders Expect from Support Groups?.Invited speaker at the Online Awares Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2012). What do Greek teachers know about learning disabilities, autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder?.Invited speaker at the Online Awares Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2012). Learning disabilities and their treatment.Invited speaker at the workshop entitled «School stress and time management» organised by the Municipality of Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2013). Eating disordered attitudes among adolescent girls with Asperger Syndrome. Invited speaker at the Second International Conference on Feeding Disorders, Middlands, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Promoting the participation of young people in the decision making. Invited speaker at AIESEC's Youth Today Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Assessment of individuals with developmental disabilities. Invited speaker at MSc in Neuroscience at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪Kalyva, E. (2014). Developmental diagnostic tools in childhood. Invited speaker at 14th Annual National Child Neurology Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Bullying in and out of the school premise. Invited Talk at the 85th Public Elementary School of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Engaging vulnerable young people in research. Invited seminar at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2015). How can our child succeed in life and in school? Invited speaker at XANTH, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2015). How to deal with behavioral problems?Invited speaker atSeminar Series “Psychology for All”, The University of Sheffield International Faculty, City College, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). "We say no to violence". Workshop organisation and delivery at the 1st Thessaloniki Science Festival (Thessaloniki, 16 & 17/5/2015)
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Working with learning disabilities. Seminar series at “Learning through play”, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Parenting children with developmental disabilities. Seminar series at “Learning through play”, Thessaloniki, Greece.
Ομιλητές μετά από κρίση της εργασίας
▪ Kalyva, E. (1996). Depression and Bereavement in Elderly People. Paper presented at the Conference of the Greek Psychological Association in Patras. It was part of a presentation on “Depression in Elderly People”.
▪ Gena, A. & Kalyva, E. (1999). Criteria for the integration of Autistic Children into Kindergarten and the First Class of Primary School. Paper presented at the Conference of the Association of Greek Psychologists in Cyprus.
▪ Kalyva, E. (1999). Psychosocial Influences on Adolescent Smoking. Poster presented at the Institute of Education, University of London.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2000). Is there hope in autism? A case study. Poster presented at the ABA Annual Convention in Washington DC.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2000). The importance of play in autism. Paper presented at the Play for all….2000 Conference in Birmingham.
▪ Kalyva, E.(2000). Psychosocial predictors of adolescent smoking. Poster presented at the BPS Developmental Section Annual Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2000). Psychosocial factors that influence adolescent smoking. Paper presented at a Conference on Developmental and Educational Psychology at the University of Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). The misconceptions that young people foster about smoking: are there gender differences? Poster presented at BPS Annual Centenary Conference in Glasgow.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). The importance of incorporating play into ABA techniques. Paper presentation at ABA Annual Convention in New Orleans.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). The importance of incorporating play in the treatment of autism. 8th Panhellenic Conference of Psychological Research in Alexandroupoli.
▪ Christidis, D.A., Zafeiri, K., Kalyva, E.,Mitsopoulou, C., Roikou, K., & Fotakopoulou, O. (2001). Training of A.P.T. students to use stress management techniques. Awarded poster presented at the 1st Panhellenic Conference of the Greek Association of Psychophysiology.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). The importance of incorporating play into ABA treatments of autistic children. Paper presented at the First International ABA Conference in Venice, Italy.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Autistic children and their parents: Facilitating their interaction through play. Paper presented at the Annual BPS Conference in Blackpool.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Peer "pressure" or peer "influence" in adolescent smoking? Poster presented at the 2002 SRA Biennial Meeting.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Adolescent smoking and health education in Greek schools.Paper presented at the ATINER conference in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). The contribution of image to the treatment of autism. Paper presented at the Conference on Icon and Child in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Improving the communication of children with autism and their peers using the “circle of friends”. Paper presented at 2nd Panhellenic Conference of Greek School Psychologists in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2003). Improving communications of children with autism and their peers at school through ‘circle of friends’ Poster presented at the BPS Annual Conference in Bournemouth.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Dimopoulou, S. (2003). Social Play in Kindergarten. Poster presented at the biannual conference of the Greek Psychological Society in Rhodes.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2003). Facilitating peer interaction of children with autism. Paper presented at the International APA Conference in Austria.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Gojkovic, D. (2003). The influence of smoking policy on adolescent smoking in Greece. Poster presented at the Xith European Conference on Developmental Psychology in Milan.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2003). The role of a mother of a child with autism. Paper presentd at the 1st Hellenic Conference on Counselling Psychology in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2004). The influence of school smoking policy on adolescent smoking in Greece. Poster presented at the IX Conference of the European Association for Research on Adolescence in Porto, Portugal.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Kasampali. A. (2004). What is the relationship between locus of control and the outcome of attempts to quit smoking?. Poster presented at the IX Conference of the European Association for Research on Adolescence in Porto, Portugal.
▪ Avramidis, E., & Kalyva, E. (2004). Greek teachers’ attitudes towards the inclusion of children with special educational needs in the mainstream school. Paper presented at the ECER Conference in Crete.
▪ Printzi, A., & Kalyva, E. (2004). The influence of the importance of the topic on the size of children’s drawings. Paper presented at the ECER Conference in Crete.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Georgiadi, M. (2004). The attitudes of mothers of typically developing children towards the inclusion of children with special needs. Paper presented at the conference “The European Dimension of Special Needs” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Avramidis, E., & Kalyva, E. (2004). The influence of teaching experience and training on Greek teachers’ attitudes towards inclusion. Paper presented at the conference “The European Dimension of Special Needs” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Papageorgiou, V., Kalyva, E., & Dafoulis, V. (2004). Hyperactivity and commorbidity in children aged between 6-9 years pld in Greece. Poster presented at the conference “The European Dimension of Special Needs” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Agaliotis, I., Kalyva, E., & Vagena, E. (2004). The use of non-verbal communication by children with SLI for the creation of social interaction: A preliminary study.Paper presented at the 5th Panhellenic Conference “Learning and teaching in an evolving society” in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E., Dimopoulou, S., & Philippou, O. (2004). The nature of solitary play in kindergarten children without siblings. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference “Quality of life and psychology” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papageorgiou, V. (2004). Greek psychology students’ knowledge about autism. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference “Quality of life and psychology” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Vucevic, A., Kalyva, E., & Brooker, C. G. (2005). How do parents discuss with their children about drug use in post-war Serbia and Montenegro? Poster presented at the BPS Quientennial Conference in Manchester.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papageorgiou, V. (2005). Improving the communication of children with autism and their peers through the ‘circle of friends’. Paper presented at the 10th Conference “Autism and communication disorders” in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2005). The influence of test anxiety on children with reading difficulties. Paper presented at the 27th ISPA Colloquium in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2005). Attitudes of typically developing children towards the inclusion of a child with motor disablitiy. Paper presented at the 11th Conference of Greek Psychological Society in Ioannina.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Dimopoulou, S. (2006). Stress experienced by parents of children with autism spectrum disorders. Paper presented at the 27th International Conference Stress and Anxiety Research Society in Crete.
▪ Karagiannidou, M., & Kalyva, E. (2006). Stress and locus of control of parents of children with nocturnal enuresis. Paper presented at the 27th International Conference Stress and Anxiety Research Society in Crete.
▪ Papageorgiou, V., Kalyva, E., & Vogindroukas, I.(2006). Health professionals’ training on autism spectrum disorders.Paper presented at the 26th International Congress of Applied Psychology in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E., Gena, A., & Tsakiris, V. (2006). Reframing the relationship between professionals and parents of children with autism using a partnership protocol. Paper presented at the 26th International Congress of Applied Psychology in Athens.
▪ Agaliotis, I, &, Kalyva, E. (2006). Can social stories affect the way children with learning disabilities resolve their interpersonal conflicts? Paper presented at the 26th International Congress of Applied Psychology in Athens.
▪ Κalyva, Ε., & Georgiadi, Μ. (2007). Bullying and Asperger: Victim or victimizer? A case study. Paper presented at the 11th Panhellenic Conference of Psychological Research in Crete.
▪ Dimopoulou, S., & Kalyva, E. (2007). The Greek standardization of the British Picture Vocabulary Scale (BPVS). Paper presented at the 9th European Conference on Psychological Assessment in Thessaloniki.
▪ Georgiadi, M., Kourkoutas, E., & Kalyva, E. (2007). Inclusion in Europe. Paper presented at the Conference “Primary Education and Contemporary Challenges” in Ioannina.
▪ Kalyva, E., Karagianni, P., Tziastas, T., Tsontaki, M., & Hatzialexiadou, E. (2007). The effect of teacher burnout on their perceptions regarding their students’ unwanted behaviours. Paper presented at the Conference “Primary Education and Contemporary Challenges” in Ioannina.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papathanasiou, E. (2007). Quality of life in children suffering from cancer in Greece. Poster presented at the 10th European Congress of Psychology in Prague.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Melonashi, E. (2007). Parental perceptions of quality of life in Albanian children with epilepsy. Poster presented at the 10th European Congress of Psychology in Prague.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Karagiannidou, M., Vassilakakis, D., & Rodopoulos, D. (2007). Quality of life in the late post-operative period after radicsl prostatectomy for localized prosate cancer. Poster presented at the 10th European Congress of Psychology in Prague.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2007). Smoking among adolescents with mild learning disabilities and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Poster presented at the 10th European Congress of Psychology in Prague.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Soulo, S. (2007). The relationship between cigarette smoking and depression among Albanian adolescents. Poster presented at the 10th European Congress of Psychology in Prague.
▪ Kalyva, E., Agaliadou, A., Evangelopoulou, E., Eliadis, P., & Karavota, M. (2007). Stress and burnout among primary schoolteachers.Paper presented at the 1st Panhellenic Conference on Clinical and Health Psychology in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). The influence of drug misuse on parenting.Paper presented at the Conference on Exploring Issues of Risk and Vulnerability to Children in South East Europe in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., Tsakiris, V., & Georgiadi, M. (2008). Comparison of eating attitudes between adolescent girls with and without Asperger syndrome: Daughters' and mothers' reports.Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on School Psychology in Rethymnon, Greece.
▪ Georgiadi, M., & Kalyva, E. (2008). The inclusion of a child with cancer in school: A case study. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on School Psychology in Rethymnon, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papathansasiou, A. (2008). Dietary habits, self esteem and body mass index of children and adolescents. Paper presented at the 1st Panhellenic Conference on Developmental Psychology in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Gena, A. (2008). Attitudes of parents of children with autism regarding their cooperation with mental health professionals.Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on “Autism: Education – Vocational Training – Work” in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Georgiadi, M. (2008). Autism and gastrointerstinal problems: Understanding the appropriateness of food.Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on “Autism: Education – Vocational Training – Work” in Athens, Greece.
▪ Papageorgiou, V., & Kalyva, E. (2008). Parents of children with autism spectrum disorders in support groups: Problems and expectations.Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on “Autism: Education – Vocational Training – Work” in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Malakonaki, E. (2009). Quality of life of children and adolescents with diabetes.Paper presented at the 12th Panhellenic Conference of Psychological research in Volos, Greece.
▪ Dafoulis, V., Kalyva, E., Kaprinis, G., Zilikis, N., & Abatzoglou, G. (2009). Psychological symptoms in children with epilepsy. Paper presented at the 2009 World Mental Health Conference in Athens, Greece.
▪ Papathanasiou, A., & Kalyva, E. (2009). Parental perceptions of the quality of life in children suffering from cancer in Greece. Paper presented at the 2009 World Mental Health Conference in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papathanasiou. A. (2009). Pediatric asthma in Greece: Impact on children’s and adolescent’s quality of life according to self and parental reports.Paper presented at the 2009 World Mental Health Conference in Athens, Greece.
▪ Georgiadi, M., Kalyva, E., & Pleksousakis, S. (2009). The transition from special to mainstream schooling: Coping strategies through the presentation of a case study. Paper presented at the Conference of Educators in Crete, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2010). Teachers’ perceptions of the sexuality of children with ASD. Paper presented at the National Conference on Special Needs Education in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., Horwath, J., & Spyrou, S. (2010). How do children and young people who were exposed to violence view participation?Paper presented at the International Conference in Childhood Studies, the 3rd Finnish Childhood Studies Conference University of Jyväskylä, Finland.
▪ Kalyva, E., Georgiadi, M., & Tsakiris, V. (2010). Counselling parents of children with autism spectrum disorders. Paper presented at the 3rd National Conference of Counselling Psychology in Crete, Greece.
▪ Savvidou, S., Kelpi, M., Kalyva, E., & Rodafinos, A. (2010). Intenret counselling as an alternative form of counseling communication. Paper presented at the 3rd National Conference of Counselling Psychology in Crete, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2010). How do children with diabetes and their parents experience quality of life?. Paper presented at the 4th Panhellenic Conference of Clinical Psychology and Psychology of Health in Athens, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2010). Teachers’ attitudes towards inclusion and their significance. Paper presented at the Conference “Special Needs Education and Psychosocial Inclusion: From School… to a Society for All” in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2011). Internet and sexuality in adolescent boys with Asperger. Paper present at the 1st Conference of Internet Addiction E-LIFE2011 in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Tasios, T. N., Kalyva, E., & Kardaras, P. (2012). Differential diagnosis of Asperger and Dyslexia based on WISC-III profiles.Paper present at the 4th Panhellenic Psychiatric Conference in Primary Health Provision in Kalamata, Greece.
▪ Kadriu, F., Kelpi, M., & Kalyva, E. (2013). Eating-disordered attitudes in Kosovo school-based populations: Potential risk factors?.Paper present at the 4th World Conference on Psychology, Counselling and Guidance, Turkey.
▪ Dafoulis, B., Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2013). Behavioral problems in children with idiopathic epilepsy. Paper present at the 8th Child Psychiatry Conference, Athens, Greece.
▪ Tasios, T. N., Kalyva, E., & Horwath, J. (2013). Redefining the democratic participation and inclusion of students in the school environment: From passive to active interaction.Paper present at the 1st International Conference Reimagining Schooling, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Papamalis, F., Kalyva, E., Meier, P., & Teare, D. (2013). Examining the impact of individual and program level factors on therapeutic process: A multidimensional framework of treatment engagement. Paper presented at the 4th Conference of European Federation of Therapeutic Communities, Prague, Czech Republic.
▪ Lukács, A., Kalyva, E., Abdul-Rasoul, M., & Barkai, L. (2014). International comparison of quality of life in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. DIABETOLOGIA HUNGARICA 22:(Suppl.2) pp. 99-101. (2014) XXII. Congress of the Hungarian Diabetes Association, Szeged, Hungary.
▪ Lukács, A., Kalyva, E., Abdul-Rasoul, M., & Barkai, L. (2014). International comparison of quality of life in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia: Clinical and Experimental Diabetes and Metabolism (ISSN: 0012-186X) (eISSN: 1432-0428) 57: (Suppl 1) p. S513. 1 p. (2014) 50th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Vienna, Austria.
▪ Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., Kalyva, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2015). The influence of motor and vocal tic severity of children’s quality of life. Paper presented at the European Pediatric Neurology Conference in Vienna, Austria.
▪ Kalyva, E., Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2015). Changes in cognitive performance in children and adolescents with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Paper presented at the European Pediatric Neurology Conference in Vienna, Austria.
▪ Kalyva, E., Tsakiris, V., Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2015). Effective interventions in addressing play deficits in children with autism spectrum disorders. Paper presented at the European Pediatric Neurology Conference in Vienna, Austria.
▪ Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., Kalyva, E., & Zafeiriou, D.I.(2015). The influence of motor and vocal tic severity at children’s quality of life. Paper presented at the 1st World Congress on TS & Tic Disorders, London, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2015). Grandparenting as a protective factor against cognitive decline. Paper presented at the Alzheimer Conference in Thessaloniki, Greece.
Ομιλίες-Ημερίδες-Workshop
Γράφτηκε από Άρης (Βλαστάρης) ΤσακίρηςΟμιλίες-Ημερίδες-Workshop

▪ Kalyva, E. (1998). Lovaas Behavioural Treatment Method for Autistic Children. Lunchtime Seminar at the Institute of Education, University of London, which addressed professors and postgraduate students who were interested in this relatively new method.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). A new model of studying smoking. Seminar presented to students and professors at the Institute of Education, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001). Alternative ways of treating autism. Seminar presented to students and professors at the Institute of Education, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2001-2002). Autism and play. Educational seminar on the importance of incorporating play into the treatment of autism, attended by professionals working in the field of autism, at the Psychiatric Hospital of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2002). Facilitating the relationship of children with autism and their parents through play. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents of children with autism and workers in autism westmidlands, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2003). Play with dolls and communication in special needs. Invited workshop at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2004). Presentation of techniques for treating children with autism. Invited workshop at the Institute of Psychiatry in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2007). Diagnosis and Treatment of Learning Disabiliites. Invited day workshop organised by the consultancy agency Employ in Thessaloniki, Greece (run twice in a month, due to big attendance).
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2007). Diagnosis and Treatment of Learning Disabiliites: Suggestions for family and school. Invited day workshop organised by the consultancy agency Employ in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2007). 1st Workshop on Interdisciplinary Research Collaboration on Cancer and Children (IRCCC): Care and Prevention. Workshop organised by South East European Research Centre in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2008). Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and treatment. Invited day workshop organised by the consultancy agency Employ in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2008). Autism and Asperger syndrome: Training in social skills. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents, educators, students, and mental health professionals at City College in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Horwath, J. (2008). Exploring Issues of Risk and Vulnerability to Children in South East Europe.Workshop organised by South East European Research Centre in Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2008). Learning disabilities: dyslexia. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents, educators, students, and mental health professionals at City College in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2008). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents, educators, students, and mental health professionals at City College in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2009). Autism and Asperger syndrome. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents, educators, students, and mental health professionals at City College in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2009). Assessment tools in education. Organisation and delivery of seminar addressing parents, educators, students, and mental health professionals at City College in Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Fereti, I. (2010). Promoting participation for vulnerable youth. Conference organised by South East European Research Centre in Athens.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2011). Counselling psychology in practice. Workshop organised at City College, Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2012). What do Greek teachers know about learning disabilities, autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder?.Invited speaker at the Online Awares Conference.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2012). Learning disabilities and their treatment.Invited speaker at the workshop entitled «School stress and time management» organised by the Municipality of Thessaloniki.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2013). Eating disordered attitudes among adolescent girls with Asperger Syndrome. Invited speaker at the Second International Conference on Feeding Disorders, Middlands, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Promoting the participation of young people in the decision makingInvited speaker at AIESEC's Youth Today Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Assessment of individuals with developmental disabilities.Invited speaker at MSc in Neuroscience at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Developmental diagnostic tools in childhood.Invited speaker at 14th Annual National Child Neurology Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Bullying in and out of the school premise. Invited Talk at the 85th Public Elementary School of Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Engaging vulnerable young people in research. Invited seminar at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, UK.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2015). How can our child succeed in life and in school? Invited speaker at XANTH, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2015). How to deal with behavioral problems?Invited speaker at Seminar Series “Psychology for All”, The University of Sheffield International Faculty, City College, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). "We say no to violence". Workshop organisation and delivery at the 1st Thessaloniki Science Festival (Thessaloniki, 16 & 17/5/2015)
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Working with learning disabilities. Seminar series at “Learning through play”, Thessaloniki, Greece.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Parenting children with developmental disabilities. Seminar series at “Learning through play”, Thessaloniki, Greece
Νοητική καθυστέρηση
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΝοητική Καθυστέρηση—Σύνδρομο Down
Νοητική Καθυστέρηση
Η νοητική καθυστέρηση πρέπει να τονιστεί ότι δεν αποτελεί μια συγκεκριμένη και αυτόνομη διαταραχή, αλλά εμφανίζεται ως πρωτεύον ή δευτερεύον σύμπτωμα πολλών άλλων διαταραχών, όπως, ο αυτισμός. Ανάλογα με την βαρύτητα της, η νοητική καθυστέρηση χωρίζεται στις παρακάτω διαβαθμίσεις:
1) Ήπια νοητική καθυστέρηση με δείκτη νοημοσύνης από 50-55 έως 70.
2) Μέτρια νοητική καθυστέρηση με δείκτη νοημοσύνης από 35-40 έως 50-55.
3) Σοβαρή νοητική καθυστέρηση με δείκτη νοημοσύνης από 20-25 έως 30-35 και
4) Βαριά νοητική καθυστέρηση με δείκτη νοημοσύνης κάτω 20 ή 25.
Ο δείκτης νοημοσύνης ή νοητικό πηλίκο υπολογίζεται με βάση τη χρονολογική και τη νοητική ηλικία του παιδιού. Ενδεικτικά αναφέρεται ότι ο φυσιολογικός δείκτης νοημοσύνης κυμαίνεται από 70 έως 130 με μέση τιμή το 100. Το ευρύτερα αποδεκτό εργαλείο αξιολόγησης της νοημοσύνης για παιδιά και εφήβους ηλικίας έως 17 ετών είναι το WISC, το οποίο χρησιμοποιούμε και στο κέντρο μας. Ωστόσο, χρησιμοποιούμε και άλλα τεστ για να αξιολογήσουμε τις επιμέρους δεξιότητες που έχει κάθε παιδί και μπορούν να αξιοποιηθούν θεραπευτικά.
Υπάρχουν πάνω από 1.000 γνωστά αίτια που προκαλούν νοητική καθυστέρηση και χωρίζονται σε δύο ομάδες. Η πρώτη ομάδα περιλαμβάνει τα οργανικά αίτια και συνδέεται συνήθως με τις πιο βαριές μορφές καθυστέρησης. Χαρακτηριστικό παράδειγμα είναι οι χρωμοσωμικές ανωμαλίες, έκφραση των οποίων είναι το σύνδρομο Down. Η δεύτερη ομάδα αιτίων περιλαμβάνει περιβαλλοντικούς παράγοντες, όπως η πολιτισμική και κοινωνική θέση της οικογένειας και συνδέεται με πιο ήπιες μορφές νοητικής καθυστέρησης. Το ποσοστό των ατόμων με νοητική καθυστέρηση ανέρχεται περίπου σε 1 έως 3% του γενικού πληθυσμού.
Σύνδρομο Down
Το σύνδρομο Downείναι η πιο κοινά αποδεκτή αιτία της νοητικής καθυστέρησης. Όπως υποδηλώνει και η χρήση του όρου σύνδρομο, αποτελεί ένα σύνολο από κοινά χαρακτηριστικά που εμφανίζονται και στο σωματικό επίπεδο και οφείλεται στη δημιουργία ενός επιπλέον χρωμοσώματος στο 21ο ζευγάρι. Η εμφάνιση του συνδρόμου Downείναι περίπου 1:770 παιδιά και εμφανίζεται κυρίως σε κυήσεις που οι μητέρες είναι ηλικίας άνω των 35 ετών. Η διάγνωση μπορεί να γίνει είτε προγεννητικά με ειδικές εξετάσεις, είτε αμέσως μετά τη γέννα, εξαιτίας των εμφανών χαρακτηριστικών του προσώπου.
Αρκετά παιδιά με σύνδρομο Downέχουν πρόβλημα στην όραση, αλλά λόγω της μικρής «γέφυρας» της μύτης δεν μπορούν να στερεώσουν τα γυαλιά τους. Είναι επιρρεπή σε κρυώματα και μολύνσεις και αρκετές φορές παρουσιάζουν απώλεια ή μείωση της ακοής, εξαιτίας χρόνιας ωτίτιδας. Δεδομένου ότι η γλώσσα του παιδιού είναι συχνά μεγαλύτερη δεν μπορεί να την κρατήσει μέσα στο στόμα και αυτό επηρεάζει την αναπνοή και την άρθρωση και κατά συνέπεια δημιουργεί προβλήματα στην ομιλία. Επειδή ο μυϊκός τους τόνος είναι πιο χαλαρός από των άλλων παιδιών, μπορεί να δυσκολεύονται στο βάδισμα, στο πήδημα, στο τρέξιμο και επομένως στη συμμετοχή σε ομαδικά κινητικά παιχνίδια. Μερικά παιδιά με σύνδρομο Downέχουν πιο κοντά και αδύνατα δάχτυλα, με αποτέλεσμα να εμφανίζουν προβλήματα στις λεπτές κινητικές δεξιότητες. Τέλος, επειδή τα περισσότερα παιδιά με σύνδρομο Downέχουν εξαιρετικά μεγάλη όρεξη, χρειάζεται ιδιαίτερη προσοχή για να μην αντιμετωπίσουν προβλήματα με το βάρος τους.
Νευροϊνωμάτωση τύπου 1
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΜαθησιακές δυσκολίες
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΜαθησιακές Δυσκολίες (Δυσλεξία)
Το παιδί με μαθησιακές δυσκολίες είναι ιδιαίτερα έξυπνο όσο αφορά τις καθημερινές του ασχολίες, αλλά δεν έχει ιδιαίτερα καλή σχολική επίδοση. Ο όρος μαθησιακές δυσκολίες είναι ιδιαίτερα ευρύς και συμπεριλαμβάνει παιδιά με ποικίλα και συχνά αντιφατικά συμπτώματα. Μερικοί άνθρωποι μπορεί να έχουν ένα ξεχωριστό μαθησιακό πρόβλημα, το οποίο δεν επηρεάζει σχεδόν καθόλου τη ζωή τους ενώ άλλοι άνθρωποι μπορεί να παρουσιάζουν ένα συνδυασμό από μαθησιακές δυσκολίες, που έχουν σημαντικές επιπτώσεις στην ακαδημαϊκή τους πορεία. Αν και οι μαθησιακές δυσκολίες εμφανίζονται σε πολύ μικρή ηλικία, η διάγνωση γίνεται συνήθως όταν το παιδί πάει στο σχολείο και δυσκολεύεται να ανταποκριθεί στις απαιτήσεις που προκύπτουν. Οι μαθησιακές δυσκολίες εμφανίζονται στο 8-10% του ελληνικού πληθυσμού και η μέση ηλικία διάγνωσης είναι η τρίτη δημοτικού.
Τα συμπτώματα που εμφανίζουν συνήθως το παιδί με μαθησιακές δυσκολίες είναι τα παρακάτω:
1) Διαβάζει αργά και συλλαβιστά χωρίς να χρωματίζει τη φωνή του, ενώ συχνά παραλείπει λέξεις ή μέρη λέξεων και αντιστρέφει γράμματα. Δεν σταματάει στις τελείες και τα κόμματα και χάνει συχνά τη σειρά στο βιβλίο. Δεν καταλαβαίνει τι διαβάζει, με αποτέλεσμα να μην μπορεί να απαντήσει σε σχετικές ερωτήσεις και να δυσκολεύεται να αποστηθίσει κομμάτια ενός κειμένου.
2) Όταν γράφει παραλείπει, προσθέτει, ή αντιστρέφει γράμματα και συλλαβές, ενώ πολλές φορές ενώνει τις λέξεις μεταξύ τους. Τα γράμματα είναι συχνά δυσανάγνωστα και λείπουν συνήθως οι τόνοι και τα υπόλοιπα σημεία στίξης. Γράφει με αργό ρυθμό και δυσκολεύεται να παρακολουθήσει την υπαγόρευση ενός κειμένου.
3) Κάνει πολλά ορθογραφικά λάθη (π.χ., κατάληξη ρήματος σε ο, ενώ εάν τον ρωτήσεις τον αντίστοιχο κανόνα της γραμματικής τον γνωρίζει). Μπορεί να γράψει την ίδια λέξη - με διαφορετικούς τρόπους κάθε φορά - ακόμα και μέσα στην ίδια παράγραφο, και ενώ του έχει επισημανθεί προηγουμένως το λάθος του.
4) Τα παιδιά με μαθησιακές δυσκολίες είναι συνήθως αρκετά ακατάστατα (όπως ακριβώς και το γραπτό τους) και στην καθημερινότητά τους, στον τρόπο που ταξινομούν τα πράγματα και στο πως βάζουν σε μία σειρά την σκέψη τους για να εκφράσουν αυτό που θέλουν. Πολύ συχνά δυσκολεύονται να συγκεντρώσουν την προσοχή τους, με αποτέλεσμα να εντείνονται ακόμα περισσότερο οι μαθησιακές τους δυσκολίες. Δυσκολεύονται επίσης στον προσανατολισμό τους μέσα σε ένα χώρο και στο συντονισμό ματιού-χεριού.
5) Πολλά παιδιά με μαθησιακές δυσκολίες έχουν χαμηλή αυτοπεποίθηση, η οποία προκύπτει από την συνεχή βίωση σχολικής αποτυχίας και αποτελεί συνήθως σοβαρότερο πρόβλημα και από την ίδια την διαταραχή. Πολλοί γονείς που θεωρούν ότι τα παιδιά τους είναι απλώς «τεμπέλικα», και δυσπιστούν για τις προσπάθειες τις οποίες καταβάλλουν, συμβάλλουν ακόμα περισσότερο στην μείωση της αυτοπεποίθησης των παιδιών τους.
Κεφάλαια σε βιβλία
Γράφτηκε από Άρης (Βλαστάρης) ΤσακίρηςΚεφάλαια σε βιβλία (με χρονολογική σειρά)
Καλύβα, Ε. (2000). Ψυχοκοινωνικές παρεμβάσεις στο κάπνισμα στην εφηβεία: Προτάσεις για παρέμβαση. Στο βιβλίο: Προκλήσεις στη σχολική κοινότητα: Έρευνα και παρέμβαση (σελ. 183-191). Αθήνα: Υπουργείο Εθνικής Παιδείας και Θρησκευμάτων: Παιδαγωγικό Ινστιτούτο.

Agorastou, M., Kalyva, E., Kaderoglou, E., & Stefanidis, F. (2009). Attitudes towards inclusion in primary education in Greece. In C. A. Marshall, E. Kendall, M. Banks, and R.M.S. Gover, Disabilities: Insights from across fields and around the world, 3 Volume book set. Westport, CT: Praeger Press.

Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2009). Developing the social skills of students with disabilities through peer tutoring: Implications for inclusion.In A.T. Heatherton and V.A. Walcott, Handbook of Social Interactions in the 21st Century (pp. 193-215).New York: Nova Publishers.

Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2011). Ways of defining and resolving peer interpersonal conflict: Applications in general and special education settings. In A. M. Columbus (Ed.), Advances in psychology research, Vol. 73. (pp. 1-26). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2011). Antisocial behavior in children with ADHD: Causes and treatment. In R. M. Clarke (Ed.), Antisocial behaviors: Causes, correlations, and treatments (pp. 75-92).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2011). Antisocial behavior in children with ADHD: Causes and treatment. In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research biographical sketches and research summaries (pp. 279-281).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2012). Teacher burnout in Greece. In: J. H. Stone and M. Blouin (Eds.), International encyclopedia of rehabilitation. Available online: http://cirrie.buffalo.edu/encyclopedia/article.php?id=124&language=en

Kalyva, E. (2012). Eating disorders in individuals with developmental disabilities. In C. M. Shapiro (Ed.), Eating disorders: Causes, diagnosis and treatments. (pp. 83-104).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2012). Sexuality for individuals with developmental disabilities. In N. E. Peterson and W. Campbell (Eds.), Handbook on sexuality: Perspectives, issues and role in society (pp. 55-74).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2012). Antisocial behavior in children with ADHD: Causes and treatment. In J. M. Turner and A. D. Mitchell (Eds.), Social psychology: New developments (pp. 113-136).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2012). Diagnosing and living with autism spectrum disorders in adulthood. In C. E. Richardson and R. A. Wood (Eds.), Autism Spectrum Disorders: New research (pp. 169-178).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Κalyva, E. (2013). The importance of choice in educating children with pervasive developmental disorders. In A. M. Columbus (Ed.), Advances in psychology research, Vol. 95. (pp. 155-166). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2013). Collaboration between parents of children with autism spectrum disorders and mental health professionals. In M. Fitzerald (Ed.,),Recent advances in autism spectrum disorders - Volume I (pp. 521-562). Prague: Intechopen.

Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2013). Social anxiety in the school setting for students with developmental disabilities. In E. Kalyva (Ed.), Social Anxiety: Perceptions, emotional and triggering symptoms and treatment(pp. 127-140). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E. (2013). Antisocial behavior in children with ADHD: Causes and treatment. In L. T. Cacioppo (Ed.), Mind and body research summaries, Vol. 3 (pp. 213-215).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Κalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2014). How do parents view the sexuality of their adolescents with high-functioning autism in Greece? The impact of culture. In M. C. Kenney (Ed.), Sex education: Attitude of adolescents, cultural differences and schools' challenges (pp. 55-74). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Social experiences of male adults with autism spectrum disorders. In A. Valdez (Ed.), Autism spectrum disorders: Early signs, interventions options and family impact (pp. 87-102). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E., Vargiami, E., & Kyriazi, M., & Zafeiriou, D.I.(2015). Autism spectrum disorders in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. In A. Costa and E. Villalba(EdS.), Horizons in Neuroscience Research. Vol. 20. Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Loneliness experienced by individuals with autism spectrum disorders In D. L. Rhodes(Ed.), Loneliness: Psychosocial risk factors, prevalence and impacts on physical and emotional health(pp. 73-90).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.

Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Empowerment and participation of children and youth with learning disabilities. In J. A. Jaworski(Ed.), Advances in Sociology Research, Vol. 17.Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2015). Eating disorders in individuals with developmental disabilities. In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research biographical sketches and research summaries (pp. 217-219).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2015). Peer interpersonal conflict resolution in children with and without disabilities. In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research biographical sketches and research summaries (pp. 301-303).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2015). Antisocial behavior in children with ADHD: Cause and treatments . In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research summaries, Vol. 3 (pp. 171-173).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E. (2015). The importance of choice in educating children with pervasive developmental disorders. In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research summaries, Vol. 4 (pp. 17349-351).Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Kalyva, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2015). Social anxiety in the school setting for students with developmental disabilities. In N. C. Wadorth and A. P. Ferguson (Eds.), Psychology research summaries, Vol. 6.Hauppage, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Περισσότερα...
Η φιλοσοφία του κέντρου μας
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΟ 'Αρης Τσακίρης και η Φρόσω Καλύβα πιστεύουμε ότι για να μπορέσουν να ξεπεραστούν σε σημαντικό βαθμό οι δυσκολίες που αντιμετωπίζουν τα παιδιά πρέπει να εφαρμοστεί μια ολιστική και εκλεκτική προσέγγιση. Αυτό σημαίνει ότι ο λόγος, η κίνηση, το συναίσθημα και η κοινωνικοποίηση πρέπει να θεωρούνται ένα σύνολο και να αντιμετωπίζονται ανάλογα.
Η αξιολόγηση γίνεται με σταθμισμένα εργαλεία (WISC-III, WIPSI, RAVEN, Αθηνά Τεστ, Bender, ADOS-2, KSADS-PL, BISCUIT, M-CHAT, PEABODY, Goodenough-Harris). Αυτό που μας ενδιαφέρει πρωτίστως είναι να φτιάξουμε ένα εξατομικευμένο πρόγραμμα διδασκαλίας που να ανταποκρίνεται στις ανάγκες, τις δυνατότητες και τα ενδιαφέροντα κάθε παιδιού και για το συγκεκριμένο λόγο φτιάχνουμε οι ίδιοι πολλά υλικά με τα οποία δουλεύουμε.
Στόχος μας είναι να περνάει καλά το παιδί στο χώρο μας και να βιώνει την επιτυχία, ενώ υπάρχουν παράλληλα πολύ ξεκάθαρα και αυστηρά όρια. Έτσι αναπτύσσεται η αυτονομία και η αυτοπεποίθηση και όχι η έλλειψη πειθαρχίας. Θεωρούμε επίσης εξαιρετικά σημαντική τη συνεργασία όχι μόνο με την οικογένεια του παιδιού, αλλά και με τους εκπαιδευτικούς του σχολείου όπου φοιτά και με άλλους επαγγελματίες που τυχόν το παρακολουθούν, προκειμένου να υπάρχει μια συνοχή και συνέχεια στη δουλειά που γίνεται.
Φιλελλήνων 1 & Βασιλίσσης Όλγας, Θεσ/νίκη,
2310 820583—6945587296
Επιστημονικά Άρθρα
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΕπιστημονικά άρθρα (σε χρονολογική σειρά)

▪ Kalyva, E. (2004). The ‘circle of friends’ as a way to improve communication between children with autism and their peers at school: A preliminary study. Issues in Special Education, 23, 34-43.
▪ Avramidis, E., & Kalyva, E. (2004). Understanding “dyslexia”: Cleaning up a messy construct and developing supportive educational environments. Use of English, 56, 25-47.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Papageorgiou, V. (2004). Psychology students’ knowledge about autism. Good Autism Practice, 5, 61-67.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Avramidis, E. (2005). Improving communication between children with autism and their peers through the ‘circle of friends’. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 18, 253-261. (impact factor: 1.385)
▪ Avramidis, E., & Kalyva, E. (2007). The influence of teaching experience and professional developmenton Greek teachers’ attitudes towards inclusion.European Journal of Special Needs Education, 22, 367-389.
▪ Kalyva, E., Georgiadi, M., & Tsakiris, V. (2007). The attitudes of Greek parents of typically developing primary schoolchildren towards inclusion.European Journal of Special Needs Education, 22, 295-305.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2007). Prevalence and influences on self-reported smoking among adolescents with mild learning disabilities, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and their typically developing peers. Journal of Intellectual Disabilities, 11, 267-279.
▪ Kalyva, E., Gojkovic, D., & Tsakiris, V. (2007). Serbian teachers’ attitudes towards inclusion. International Journal of Special Education, 22, 30-35.
▪ Georgiadi, M., Kourkoutas, E., & Kalyva, E. (2007). Inclusion in Europe. Paper published at the proceedings of the Conference “Primary Education and Contemporary Challenges” in Ioannina, pp. 1236-1243.
▪ Kalyva, E., Karagianni, P., Tziastas, T., Tsontaki, M., & Hatzialexiadou, E. (2007). The effect of teacher burnout on their perceptions regarding their students’ unwanted behaviours. Paper published at the proceedings of the Conference “Primary Education and Contemporary Challenges” in Ioannina, pp. 1279-1283.
▪ Papageorgiou, V., Kalyva, E., Dafoulis, V., & Vostanis, P. (2008). Parent and teacher ratings of hyperactivity and other mental health problems in 6-9 year old Greek children. European Journal of Psychiatry, 22, 200-210. (impact factor: 0.46)
▪ Agaliotis, I., & Kalyva, E. (2008). Nonverbal social interaction skills of children with learning disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 29, 1-10. (impact factor: 3.405)
▪ Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2009). Can social stories enhance the interpersonal conflict resolution skills of children with LD?Research in Developmental Disabilities, 30, 192-202. (impact factor: 3.405)
▪ Kalyva, E. (2009).Comparison of eating attitudes between adolescent girls with and without Asperger syndrome: Daughters' and mothers' reports. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 480-486. (impact factor: 3.341)
▪ Kalyva, E., & Agaliotis, I. (2009). Can contact affect Greek children's understanding of and attitudes towards peers with physical disabilities? European Journal of Special Needs Education, 24, 213-220.
▪ Kalyva E. 2010. Special Education: What do Greek Teachers Know about Learning Disabilities, Autism, and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder?. In: JH Stone, M Blouin, editors. International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation. Available online: http://cirrie.buffalo.edu/encyclopedia/en/article/263/
▪ Kalyva, E., Pellizzoni, S., Tavano, A., Iannello, P., & Siegal, M. (2010). Contamination sensitivity in autism, Down syndrome, and typical development. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4, 43-50. (impact factor: 2.959)
▪ Kalyva, E. (2010). Teachers’ perspectives of the sexuality of children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4, 433-437. (impact factor: 2.959)
▪ Papageorgiou, V., & Kalyva, E. (2010). Self-reported needs and expectations of parents of children with autism spectrum disorders who participate in support groups. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4, 653-660. (impact factor: 2.959)
▪ Kalyva, E. (2010). Mutlirater congruence on the social skills assessment of children with Asperger Syndrome: Self, mother, father, and teacher Ratings. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 1202-1208. (impact factor: 3.341)
▪ Kalyva, E., Malakonaki, E., Eiser, C., & Mamoulakis, D. (2011). Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL) of children with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM): Self and parental perceptions. Pediatric Diabetes, 12, 34-40. (impact factor: 2.171)
▪ Agaliotis, I., & Kalyva, E. (2011). A survey of Greek general and special education teachers’ perceptions regarding the role of the special needs coordinator: Implications for educational policy on inclusion and teacher education. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27, 543-51. (impact factor: 1.322)
▪ Horwath, J., Kalyva, E., & Spyrou, S. (2012). “I want my experiences to make a difference” promoting participation in policy-making and service development by young people who have experienced violence. Children and Youth Services Review, 34, 155-162. (impact factor: 1.269)
▪ Dafoulis, V., & Kalyva, E. (2012). Factors associated with behavioral problems in children with idiopathic epilepsy. Epilepsy Research, 100, 104-112. (impact factor: 2.302)
▪ Georgiadi, M., Kalyva, E., Kourkoutas, E., & Tsakiris, V. (2012). Young children’s attitudes toward peers with intellectual disabilities: Effect of the type of school. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 25, 531-541. (impact factor: 1.385)
▪ Papoutsaki, K., Gena, A., & Kalyva, E. (2013). How do children with mild intellectual disabilities perceive loneliness? Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 9, 51-61.
▪ Kalyva, E. (2013). Stress in Greek primary schoolteachers working under conditions of financial crisis. Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 9, 104-112.
▪ Zafeiriou, D., Ververi, A., Dafoulis, V., Kalyva, E., & Variami, E. (2013). Autism Spectrum Disorders: The quest for genetic syndromes. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 122, 327-366. (impact factor: 3.231)
▪ Zafeiriou, D.I,, Ververi, A., Vargiami, E., Kalyva, E., Kyriazi, M., Gioula, G., Gerou, S., Al-Mutawa, H., & Kambouris, M. (2013). Mild phenotype and high-functioning autism in a boy with MECP2 duplication syndrome.European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 17: Supplement 1, S117-120. (impact factor: 1.93)
▪ Kalyva, E. (2014). Is research on mental health relevant to culture and context? Clinics in Mother and Child Health, 11, 1.
▪ Kalyva, E., Vargiami, E., Kyriazi, M., & Zafeiriou, DI. (2013). Cognitive and executive profile in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatrics, 76, 414-423.
▪ Kadriu, F., Kelpi, M., & Kalyva, E. (2014). Eating-disordered attitudes in Kosovo school-based populations: Potential risk factors. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 114, 382-387.
▪ Kalyva, E., & Melonashi, E. (2014). Reported maternal styles and substance abuse: A cross-sectional study among educated Albanian young adults. Substance Use and Misuse, 49, 654-660. (impact factor: 1.109)
▪ Kalyva, E., & Melonashi, E. (2015). Parental perceptions of health-related quality of life of Albanian children with epilepsy. Health Psychology Research, 3, 22-44.
▪ Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., Kalyva, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2015). The influence of motor and vocal tic severity of children’s quality of life. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 19, S81..(impact factor: 1.93)
▪ Kalyva, E., Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., & Zafeiriou, D.I.(2015). Changes in cognitive performance in children and adolescents with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 19, S91.
(impact factor: 1.93)
▪ Kalyva, E., Tsakiris, V., Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2015). Effective interventions in addressing play deficits in children with autism spectrum disorders. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 19, S94. (impact factor: 1.93)
▪ Kalyva, E., Abdul-Rasoul, M., Kehl, D., Barkai, L., & Lukacs, A. (2015). A cross-cultural study on perceived health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.12.021 (impact factor: 3.005)
▪ Kalyva, E., Kyriazi, M., Vargiami, E., & Zafeiriou, D. I. (2016). A review of co-occurrence of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Tourette Syndrome. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4, 653-660. (impact factor: 2.959)
Διαταραχή του Φάσματος του Αυτισμού (κλασικός αυτισμός - σύνδρομο Asperger)
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΔιαταραχή του Φάσματος του Αυτισμού (κλασικός αυτισμός - σύνδρομο Asperger)
Η διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού χαρακτηρίζεται από έντονες ελλείψεις στην κοινωνική επικοινωνία και στην κοινωνική αλληλεπίδραση σε ποικίλα πλαίσια, καθώς και από περιορισμένα και επαναλαμβανόμενα μοτίβα συμπεριφοράς, ενδιαφερόντων ή δραστηριοτήτων.
Οι γονείς ενός παιδιού με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού αναφέρουν συνήθως, ότι ως βρέφος δεν επιζητούσε την αγκαλιά και το βλέμμα του ήταν κάπως απόμακρο. Αρκετοί μάλιστα πίστευαν ότι το παιδί τους είχε πρόβλημα ακοής, επειδή έδειχνε να μην αντιδρά σε θορύβους ή άλλα ερεθίσματα του περιβάλλοντος. Οι ανησυχίες τους αυξήθηκαν κυρίως όταν το παιδί δεν ανέπτυξε καθόλου λόγο ή παρέμεινε στη χρήση απλών λέξεων χωρίς επικοινωνιακή πρόθεση.
Επισημαίνοντας εκ νέου ότι τα συμπτώματα διαφέρουν ως προς το βαθμό εκδήλωσής τους, τα πιο συνηθισμένα και χαρακτηριστικά συμπτώματα της διαταραχής του φάσματος του αυτισμούείναι τα ακόλουθα:
1) Το παιδί με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού έχει ανάγκη από ένα σταθερό και αμετάβλητο περιβάλλον. Θέλει τα πράγματα να βρίσκονται σε συγκεκριμένο χώρο με συγκεκριμένη διάταξη και αντιδρά έντονα σε οποιαδήποτε αλλαγή του περιβάλλοντος ή του καθημερινού του προγράμματος.
2) Παρατηρείται έντονη στερεοτυπία είτε με τη μορφή λικνίσματος μπρος πίσω είτε με τίναγμα των χεριών, είτε με κύκλους που κάνει το παιδί γύρω από τον εαυτό του.
3) Το παιδί με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού είναι συχνά απομονωμένο και δεν επιζητά την επαφή με άλλους ανθρώπους. Αποφεύγει την βλεμματική επαφή και δεν είναι ιδιαίτερα ανοιχτό σε αγκαλιές και άλλου είδους εκδηλώσεις τρυφερότητας. Τα παιδιά με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού που επιχειρούν να προσεγγίσουν συνομηλίκους τους χρησιμοποιούν συνήθως έναν ιδιόρρυθμο τρόπο, με αποτέλεσμα η προσέγγιση να είναι ανεπιτυχής.
4) Αρκετά παιδιά με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού δεν κατορθώνουν να αναπτύξουν τον λόγο ενώ αρκετά παιδιά έχουν ιδιοσυγκρασιακό λόγο με επαναλαμβανόμενες λέξεις ή προτάσεις. Πολύ συχνή στα παιδιά με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού είναι και η εμφάνιση της ηχολαλίας (επαναλαμβανόμενες λέξεις ή φράσεις), η οποία γίνεται χωρίς κάποια πρόθεση για επικοινωνία. Το παιδί με διαταραχή του φάσματος του αυτισμού αποφεύγει συνήθως να ξεκινήσει μία συζήτηση και δυσκολεύεται να διατηρήσει ένα διάλογο και να μοιραστεί τις σκέψεις και τα συναισθήματά του. Παρουσιάζει επίσης δυσκολίες στην κατανόηση μη-λεκτικών μέσων επικοινωνίας, όπως είναι οι χειρονομίες, οι εκφράσεις του προσώπου και η στάση του σώματος.
5) Πολλά παιδιά με αυτισμό θεωρείται ότι έχουν ταυτόχρονα και νοητική καθυστέρηση. Ωστόσο, πρέπει να επισημανθεί ότι είναι πολύ δύσκολο να αξιολογηθεί η νοητική ανάπτυξη ενός παιδιού που δεν επικοινωνεί καθόλου με το περιβάλλον ή έχει περιορισμένες δυνατότητες επικοινωνίας. Τα παιδιά με σύνδρομο Asperger ή αυτισμό υψηλής λειτουργικότητας μπορεί να παρουσιάζουν αρκετά από τα παραπάνω συμπτώματα, έχει όμως αποδειχθεί ότι η νοημοσύνη τους είναι μέσα στα κανονικά για την ηλικία τους επίπεδα.
Το βιβλίο της Δρ Ευφροσύνης Καλύβα με τίτλο "Αυτισμός: Εκπαιδευτικές και θεραπευτικές προσγγίσεις" που κυκλοφορεί από τις εκδόσεις Παπαζήση έχει πολλές πληροφορίες για την αποτελεσματικότητα προτεινόμενων θεραπειών.
Διάσπαση προσοχής
Γράφτηκε από Δρ. Φρόσω (Ευφροσύνη) ΚαλύβαΔιαταραχή Ελλειμματικής Προσοχής / Υπερκινητικότητα (ΔΕΠΥ)
Η Διαταραχή Ελλειμματικής Προσοχής / Υπερκινητικότητα παρουσιάζει έξαρση τα τελευταία χρόνια και σύμφωνα με την τελευταία έκδοση των διαγνωστικών κριτηρίων κατά DSΜ-5 εκδηλώνεται με 3 διαφορετικές εκφάνσεις: Α. Σύνδρομο ελλειμματικής προσοχής, Β. Σύνδρομο υπερκινητικότητας, και Γ. Σύνδρομο ελλειμματικής προσοχής με υπερκινητικότητα
Τα κύρια συμπτώματα της ΔΕΠΥ ανάλογα με τον τύπο στον οποίο ανήκει το παιδί είναι τα παρακάτω:
Α) Σύνδρομο Ελλειμματικής Προσοχής
1) Δεν μπορεί να συγκεντρώσει την προσοχή του σε λεπτομέρειες με αποτέλεσμα να κάνει πολλά λάθη από απροσεξία στις εργασίες του σχολείου.
2) Αδυνατεί να ακολουθήσει τις οδηγίες που του δίνουν, χωρίς αυτό να οφείλεται σε αδυναμία κατανόησης των οδηγιών.
3) Δεν μπορεί να βάλει σε μία τάξη τις εργασίες του και τα καθήκοντα που του αναθέτει κάποιος.
4) Ακόμα και όταν ασχολείται με κάτι που του αρέσει ή όταν παίζει δυσκολεύεται να διατηρήσει την προσοχή του.
5) Όταν κάποιος του απευθύνει τον λόγο δίνει την εντύπωση ότι είναι αφηρημένος, ενώ παράλληλα ξεχνά πολλές φορές τις καθημερινές του δραστηριότητες.
6) Αποσπάται εύκολα η προσοχή του από εξωτερικά ερεθίσματα, γεγονός που καθιστά ιδιαίτερα δύσκολη τη δραστηριοποίησή του σε μία γενική τάξη γεμάτη θορύβους.
7) Χάνει αντικείμενα τα οποία του είναι απαραίτητα για να αντεπεξέλθει στις εργασίες του, χωρίς να υπάρχει κάποια ιδιαίτερη σκοπιμότητα.
Β) Σύνδρομο Υπερκινητικότητας
1) Δεν θέλει να μείνει στο ίδιο μέρος για πολύ χρονικό διάστημα και συχνά τρέχει από τη μία πλευρά του δωματίου στην άλλη.
2) Μιλάει υπερβολικά και γρήγορα χωρίς να περιμένει να του απευθύνει κάποιος τον λόγο ή να ολοκληρώσει την ερώτηση.
3) Παίζει νευρικά με τα χέρια του, στριφογυρίζει στην θέση του, κουνάει συνεχώς τα πόδια του ή απασχολεί τα χέρια του διαρκώς με αντικείμενα.
4) Δυσκολεύεται να συμμετέχει σε ομαδικές ή ατομικές δραστηριότητες και να παίξει με ηρεμία. Στα ομαδικά παιχνίδια θέλει να επιβάλει την παρουσία του και δυσκολεύεται να περιμένει την σειρά του. Είναι χαρακτηριστικό ότι συνήθως σπάει και χαλάει τα παιχνίδια του, ακόμα και όταν είναι τα αγαπημένα του.
5) Κοιμάται πολύ αργά και ξυπνάει νωρίς, αλλά δεν εμφανίζει σημάδια κόπωσης στη διάρκεια της μέρας. Μπορεί για παράδειγμα να ανεβαίνει κάθε μέρα στα έπιπλα και να πηδάει από το ένα στο άλλο.
Τα παιδιά που έχουν σύνδρομο ελλειμματικής προσοχής με υπερκινητικότητα παρουσιάζουν συμπτώματα και από το Α) και από το Β). Όπως είναι φυσικό, οι συμπεριφορές που αναφέρθηκαν επηρεάζουν αρνητικά τη διαπροσωπική, τη σχολική, την κοινωνική και την επαγγελματική εικόνα και απόδοση του παιδιού. Πολλά παιδιά με ΔΕΠΥ έχουν μαθησιακές δυσκολίες και χαμηλή αυτοπεποίθηση και οι γονείς τους δηλώνουν συχνά εξαντλημένοι από τη φροντίδα τους.















